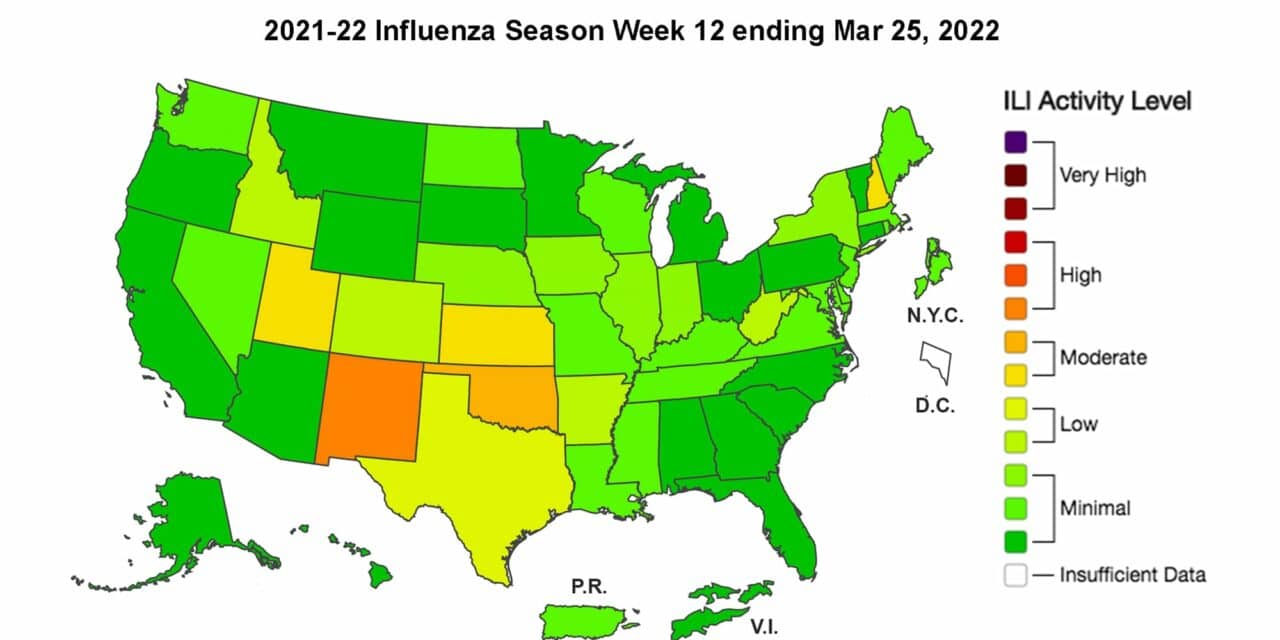
Influenza activity is increasing in the northeast and northwest regions with the highest activity in the central and south-central regions of the country.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s FluView report shows that the majority of influenza viruses detected are A(H3N2) and are genetically closely related to the vaccine virus. A little over 6% of all samples tested this week were positive for influenza, higher than the overall season average of 3.2%.
Antigenic data show that most of the H3N2 viruses in circulation are antigenically distinct from the vaccine reference viruses. While the number of B viruses circulating this season is small, most of the B viruses are antigenically similar to the vaccine reference virus, the FluView report shows.
The number of outpatient visits due to respiratory illness was stable this week compared with last week and remains below the baseline.
The CDC warns that while influenza is contributing to levels of respiratory illness, other respiratory viruses are also circulating. The relative contribution of flu viruses varies by region and health authorities continue to recommend the flu vaccine as a first-line defense.
The CDC data also show that the number of hospital admissions reported has increased each week for the past eight weeks. Cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than the rate for the entire 2020-2021 season, but lower than during the four seasons preceding the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the FluView report, one influenza-associated pediatric death was reported this week. In total, 14 pediatric deaths have been documented this season.
Health officials estimate that, so far this season, there have been at least 3.5 million influenza illnesses, 34,000 hospitalizations, and 2,000 deaths related to influenza.