Dexamethasone, a common steroid used to treat arthritis and other disorders, successfully reduced COVID-19 mortality in critical care patients receiving ventilation and supplemental oxygen, according to preliminary study results from the University of Oxford.
As part of the RECOVERY (Randomized Evaluation of COVid-19 thERapY) randomized clinical trial, over 11,500 patients were enrolled from over 175 NHS hospitals in the UK.
A total of 2,104 patients were randomized to receive dexamethasone 6 mg once per day (either by mouth or by intravenous injection) for 10 days and were compared with 4,321 patients randomized to usual care alone.
Among the patients who received usual care alone, 28-day mortality was highest in those who required ventilation (41%), intermediate in those patients who required oxygen only (25%), and lowest among those who did not require any respiratory intervention (13%).
According to the study, dexamethasone reduced deaths by one-third in ventilated patients and by one-fifth in other patients receiving oxygen only. There was no benefit among those patients who did not require respiratory support.
Based on these results, 1 death would be prevented by treatment of around 8 ventilated patients or around 25 patients requiring oxygen alone, the researchers concluded.
“Dexamethasone is the first drug to be shown to improve survival in COVID-19. This is an extremely welcome result,” said Peter Horby, Professor of Emerging Infectious Diseases in the Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, and one of the Chief Investigators for the trial. “The survival benefit is clear and large in those patients who are sick enough to require oxygen treatment, so dexamethasone should now become standard of care in these patients. Dexamethasone is inexpensive, on the shelf, and can be used immediately to save lives worldwide.”
Martin Landray, Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology at the Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, one of the Chief Investigators, said: ‘Since the appearance of COVID-19 six months ago, the search has been on for treatments that can improve survival, particularly in the sickest patients. These preliminary results from the RECOVERY trial are very clear –dexamethasone reduces the risk of death among patients with severe respiratory complications. COVID-19 is a global disease — it is fantastic that the first treatment demonstrated to reduce mortality is one that is instantly available and affordable worldwide.”
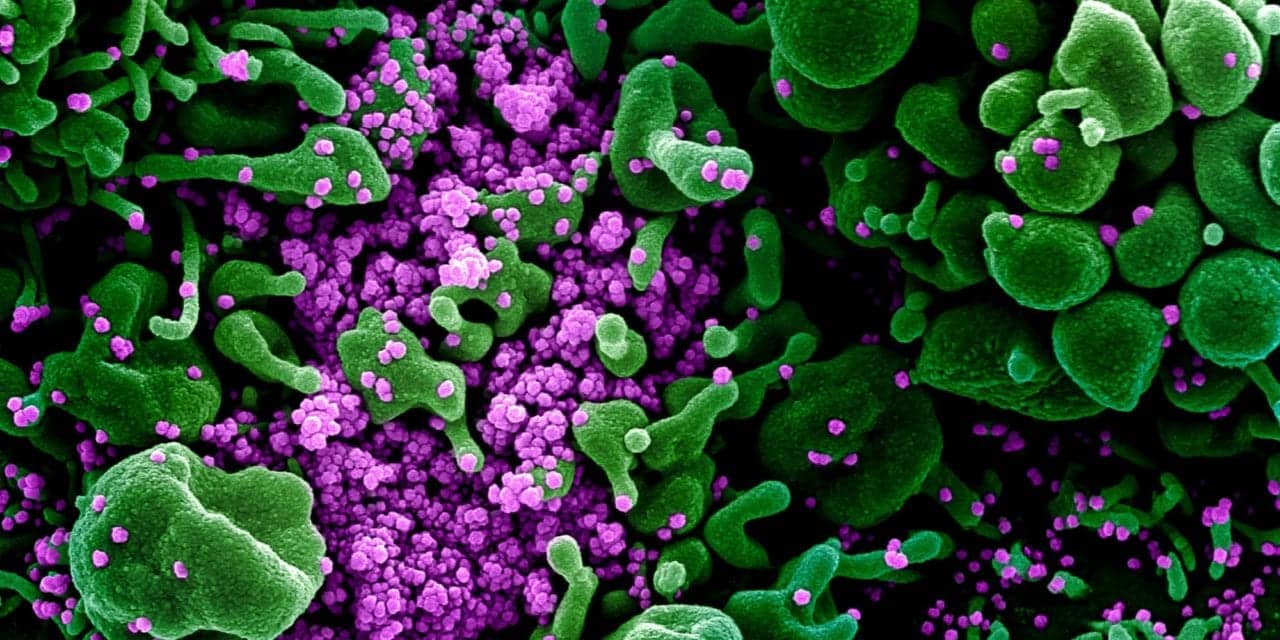
Image credit: NIAID. Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Colorized scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic cell (green) heavily infected with SARS-COV-2 virus particles (purple), isolated from a patient sample. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland.