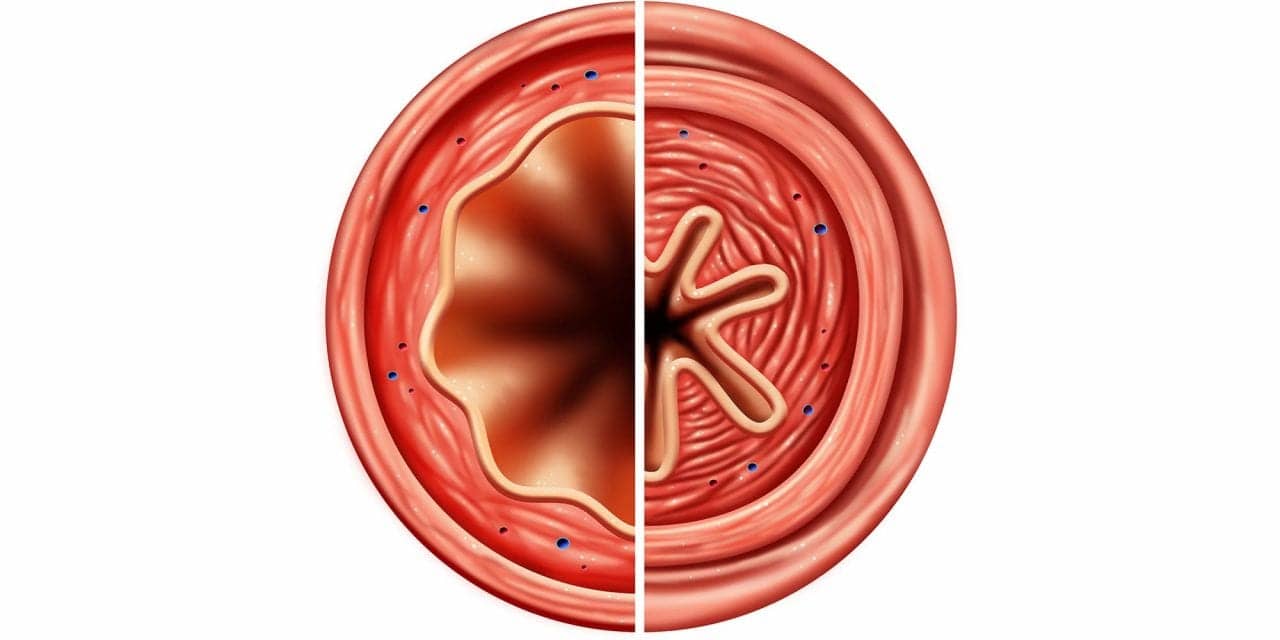
Researchers say a protein secreted by larvae of the roundworm Heligmosomoides polygyrus bakeri (Hpb) has an anti-inflammatory effect that should be investigated as an allergic asthma therapy.
“The ability of Hpb glutamate dehydrogenase to weaken the immune response makes it a promising candidate for treatment of chronic airway inflammation,” researchers said.
The researchers used a mouse model of allergic asthma to successfully show that the larval protein can be used to suppress inflammatory reactions.